Describing HBase
- As a reminder, HDFS is a file system
- HBase is a database
- Specifically, it is a distributed NoSQL database
- It is built on top of (but separate from) HDFS
- HBase is used for providing real-time, read/write access to HDFS
- Roughly, we can think of HBase as the database form of the unstructured file system that is HDFS
- A server on which a
NameNodelives is called a master server - A server on which a
DataNodelives is called a region server
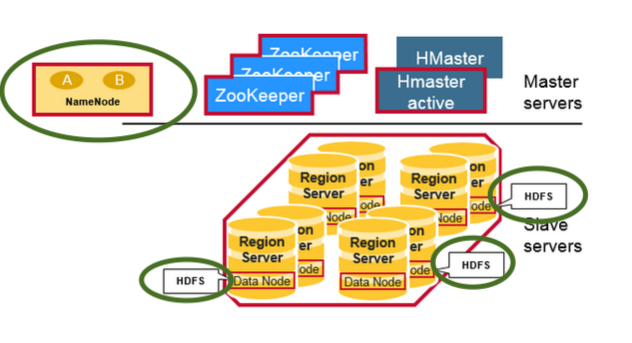
Defining the Components of HBase
- HMaster Nodes
- Region Servers
- ZooKeeper Nodes
Describing HBase HMaster Nodes
-
HMaster nodes are responsible for:
- Coordinating region servers in the cluster
- Negotiating load balancing across region servers
- Executive administrative operations
- Maintaining the state of its cluster
- Monitoring the state of its cluster
- These nodes are not included in the region servers
- Meaning, they are not part of the actual data storage
- Instead, they manage and monitor the state of hadoop clusters
Describing Region Servers
-
Region servers are responsible for:
- Handling a subset of the table's data
- These are nodes that host data and process I/O requests
Describing ZooKeeper Nodes
-
Zookeeper nodes are responsible for:
- Coordinating between the HMaster nodes and region servers
- Coordinate data retrieval from region servers
- Monitoring any session timeouts
- Monitoring the statuses of nodes in the cluster by checking for heartbeats
Motivating use cases of HBase over HDFS
-
Hadoop is basically things
- A file system (i.e. HDFS)
- A computation framework (i.e. MapReduce)
- A management bridge (i.e. YARN)
-
HDFS is used for:
- Storing huge amounts of data
- Ensuring the data is distributed
- Ensuring the data is redundant
- HDFS is good for sequential data access (reads/writes)
-
However, it is not good for random data access (reads/writes)
- This is because it is only a file system
- HBase is good for real-time, random data access
Comparing HBase to HDFS
- HBase stores both structued and unstructured data
- HDFS also stores structured and unstructured data
-
Both provide multiple mechanisms to access data:
- Shell
- APIs
- HBase stores data as key/value pairs in a columnar fashion
- HDFS stores data as flat files
-
HDFS supports the following:
- Optimized for streaming access of large files
- Follows write-once, read-many ideology
- Doesn't support random read/write
-
HBase supports the following:
- Stores key/value pairs in columnar fashion
- Provides a flexible data model
- Supports random read/write
- Provides low latency access to small amounts of data from large datasets
-
To summarize:
- HDFS is used for offline batch-processing
- HBase is used for real-time reads and writes
References
Previous
Next