Describing Hadoop MapReduce
- MapReduce is a component of the Hadoop ecosystem
- It is a software framework
- It is used for processing vast amounts of data
-
It ensures data is processed:
- In a distributed manner
- In parallel
- On large clusters
- Using cheap hardware
- Reliably
- In a fault-tolerant manner
Distributed Computing with MapReduce
-
MapReduce is consists of two functions:
- A
mapfunction - A
reducefunction
- A
-
In Hadoop:
- MapReduce is a distributed computing framework
- HDFS is a distributed storage framework
- As a result, the
mapandreducefunctions run on many different computers
Defining the MapReduce Algorithm
-
A
mapfunction- Takes in data from each
DataNodeas input -
Outputs key-value pairs
- A key is a piece of data from the
DataNode - A value is an aggregation from the
DataNode
- A key is a piece of data from the
- Each value only measures an aggregation of an individual
DataNode
- Takes in data from each
-
A
reducefunction- Takes in key-value pairs for each
DataNode -
Outputs updated key-value pairs from all
DataNodes- A key is a piece of data from all
DataNodes - A value is an aggregation from all
DataNodes
- A key is a piece of data from all
- Takes in key-value pairs for each
Illustrating MapReduce by Counting Words
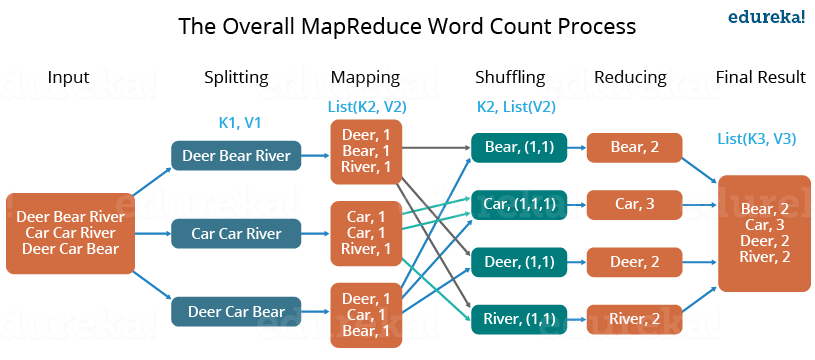
Describing Components of MapReduce Implementation
-
A MapReduce application consists of two main services:
- One
JobTracker - Some
TaskTrackers
- One
-
A
JobTrackerhas the following properties:- It acts like a master-server
- It communicates with the
NameNode - It ensures the execution of submitted jobs is completed
-
A
TaskTrackerhas the following properties:- It communicates with the
DataNodes - It is responsible for performing the actual service
- Meaning, it performs mapping, shuffling, and reducing tasks
- It communicates with the
Defining the MapReduce Workflow
-
Client submits an application to the
JobTracker- The
JobTrackerseparates the application into tasks - These tasks include the
map,reduce,shufflefunctions
- The
-
That
JobTrackerrequests metadata from itsNameNode- This metadata includes the location of relevant data
-
The
NameNodeprovides theJobTrackerwith metadata- This metadata has data about the location of
DataNodes - Only the
DataNodeswith any relevant data are included
- This metadata has data about the location of
-
The
JobTrackerlocates availableTaskTrackers-
It tries to find
TaskTrackersthat are:- Available
- Closest to the relevant
DataNodesas possible
-
-
The
JobTrackersubmits its tasks to theTaskTrackers- Only the chosen
TaskTrackersare included
- Only the chosen
-
The
TaskTrackersexecute any individual tasks- They communicate with their specified
DataNodes TaskTrackerssend progress reports to theJobTracker- They do this by sending heartbeat signals
- If the
JobTrackerdoesn't receive a heartbeat signal, it will assume theTaskTrackerhas failed - Then, it will reschedule its task and start a new
TaskTracker
- They communicate with their specified
-
The
TaskTrackerscomplete all individual tasks- They update the
JobTracker
- They update the
-
The
JobTrackerupdates its status to complete- Client applications can poll the
JobTrackerfor information now
- Client applications can poll the
References
Previous
Next