Describing Hadoop YARN
- YARN is a component of the Hadoop ecosystem
-
YARN is used for:
- Managing computing resources in a cluster
- Monitoring computing resources in a cluster
- Scheduling jobs involving processing
- It manages and monitors resources via
NodeManagers - A job refers to a requested transformation
- An example of a job is a MapReduce job
- An application consists of one or many jobs
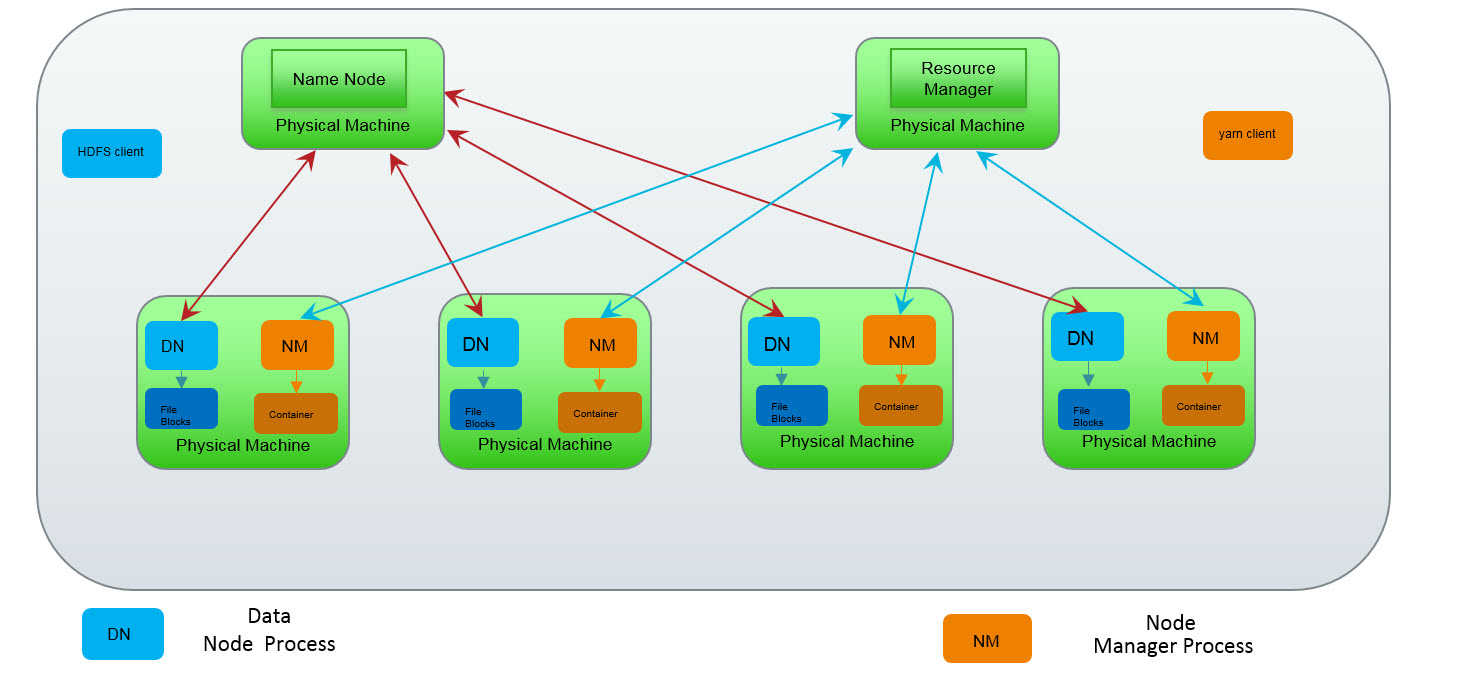
Describing the YARN Architecture
-
YARN consists of:
- Many different nodes in a cluster
- Separate daemons living on those nodes
- A node represents a single computer or server
- A cluster represents a collection of nodes
- These nodes are all interconnected with each other
-
The YARN daemons are:
ResourceManagerNodeManagersApplicationMasters- Containers
- Typically, containers host any MapReduce job
- These jobs involve transforming blocks on
DataNodes NodeManagersare used for overseeing its container
How YARN Handles Resource Management
-
Resource management in YARN mostly is handled by:
- A
ResourceManager - Some
NodeManagers
- A
-
A
ResourceManageris used for:- Initializing an
ApplicationMaster - Initializing containers
- Allocating requested resources to an
ApplicationMaster -
Recording information about:
- Available resources
- Resources allocated to applications in the cluster
- Initializing an
-
A
NodeManageris used for:- Monitoring containers on its node
- Restoring failed containers on its node
-
Reporting usage of resources to the
ResourceManager- CPU resources
- Memory resources
- Disk resources
- Network resources
- Initializing containers on its node
- Typically, there is a single
ResourceManagerin a cluster - Typically, there is a single
NodeManagerper node
How YARN Handles Job Scheduling
-
Job scheduling in YARN mostly is handled by:
- Some
ApplicationMasters - Some containers
- Some
-
An
ApplicationMasteris used for:- Requesting for additional or fewer resources from the
ResourceManager - Allocating these resources to its containers
- Monitoring its application
- Requesting for additional or fewer resources from the
-
Containers are used for:
- Running an assigned application
- Reporting the application status to the
ApplicationMaster
- Typically, there is a single
ApplicationMasterper application
Illustrating the YARN Workflow
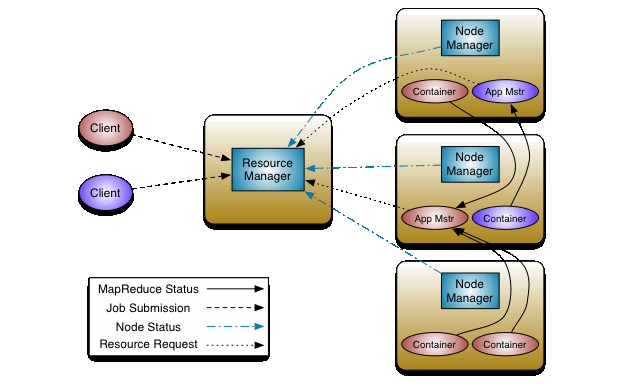
Defining the YARN Workflow
- Client submits an application
- The
ResourceManagerinitializes a container -
The
ResourceManagerinitializes anApplicationMaster- There is an
ApplicationMasterfor each container
- There is an
-
An
ApplicationMasterrequests resources from theResourceManager- It uses these resources for itself and its containers
-
The
ApplicationMasterreceives resources- It uses these resources for itself and its containers
-
The
AMnotifies theNMto launch containers- These containers run the application (MapReduce jobs)
- Containers running
maptasks are run on the same node as the relevant blocks - Containers running
reducetasks sometimes run on different nodes - Containers running
reducetasks start aftermaptasks
-
The applications request metadata from the
NameNode- Only metadata of relevant blocks in
DataNodesis returned - These applications are executed in the containers
- Only metadata of relevant blocks in
-
The applications receive metadata from the
NameNode- Only metadata of relevant blocks in
DataNodesis received - These applications are executed in the containers
- Only metadata of relevant blocks in
-
Each daemon monitors resources
- The
ResourceManagermonitors the cluster's status - The
ApplicationMastermonitors its application's status - The
NodeManagermonitors its node's status
- The
- The application is complete
- The
ApplicationMasterunregisters itself from theResourceManager
References
Previous
Next